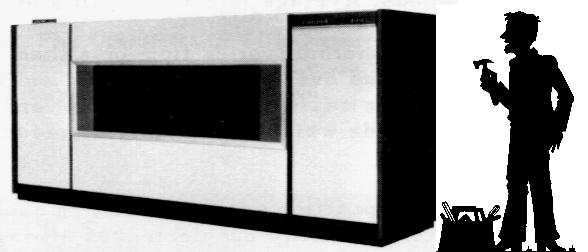

The FASTRAND II random-access mass storage system was one of the most impressive peripherals ever attached to a commercial computer. Used with the UNIVAC 1108 computer, it provided the first permanent file storage capability in the UNIVAC 1100 series family.
No UNIVAC programmer who ever encountered a FASTRAND is likely to forget it. It was big, heavy (it weighed about two and a quarter tons, and required special reinforcement of the raised floor it sat on), had a large window lit by fluorescent lights which let you see the two huge drums rotating in opposite directions at 880 revolutions per minute and the heads jumping back and forth as various tracks were accessed. In operation, it emitted a deep rumble accompanied by a whoosh of air much like the engine room in Star Trek. Opening the door on the end revealed a complex control panel which included, at the top, a collection of “hit detectors” which told you if one of the read/write heads had contacted the drum surface.
| Storage Capacity | 22,020,096 36-bit words; 132,120,576 6-bit characters, or about 90 megabytes¹ |
|---|---|
| Drum Speed | 880 revolutions per minute |
| Read/write heads | 64, on a movable boom between the two drums |
| Average access time | 92 milliseconds |
| Transfer rate | 26,283 36-bit words per second, about 100 kilobytes¹ per second |
| Recording density | 1000 bits per inch |
| Track density | 105 tracks per inch |
| Price (1968 dollars) | Controller: $41,680, Storage unit: $134,400 Maximum 8 storage units per controller |
Another odd aspect of the FASTRAND was that it addressed data in blocks, or sectors of 28 36-bit words. Most storage peripherals on binary computers use a sector size which is a power of two, for example 32 or 256. If the sector size is a power of two, address computation, such as figuring out which sector to read and which word within it to access when presented with a word address in a file, can be done entirely by shifting and masking, which is almost always much faster than multiplying or dividing. For example, on the UNIVAC 1108, division took 10.125 microseconds, while a double-word shift of any number of bits required just 0.875 microseconds: eleven and a half times faster.
Nobody ever seemed to know why the FASTRAND used 28 word sectors; the most common explanation was that the device had originally been designed to work with UNIVAC 490 series real-time computers with a word length of 30 bits and a FASTRAND sector size of 32. This may be the case, but the arithmetic doesn't quite work. If you take the number of bits corresponding to 28 36-bit words (1008), then divide by 30, you get a capacity of 33.6 30-bit words in the same sector. Why would they have wasted a word and a half in every sector? A device designed for 32 30-bit words would have a sector size of 26 36-bit words, with two-thirds of a word being wasted. Another purported explanation was that the FASTRAND had originally been designed for 32 word sectors, but wasn't reliable enough at the recording density that required, so the sector size was reduced to reduce bits per inch to a point where the hardware worked acceptably.
Whatever the reason, the number 28 was never far from the mind of a UNIVAC systems programmer, since the EXEC-8 operating system made no attempt to sugar-coat the properties of the underlying hardware. When programming in assembly language, one allocated buffers as multiples of 28 words, calculated addresses by multiplying and dividing by 28 (one wag expressed surprise when the 1110 did not include special hardware for multiplying and dividing by 28), and since word-addressable drums were usually treated as high-speed FASTRAND emulators, the influence of 28 crept throughout the system, to the block sizes used on tape drives transferring data to and from the FASTRAND.
Twenty-eight was referred to in jest as “von Fastrand's number”, after the (mythical) Baron Gustav von Fastrand, who it was said, discovered the number during a nineteenth-century expedition between the numbers 27 and 29. Even after the last FASTRAND had been long retired, its legacy, twenty-eight, lived on in UNIVAC 1100 Series software. Byte-oriented disc drive controllers had special hardware to repack 36-bit words efficiently into 8-bit bytes, and physical sector sizes, expressed in words, were always a multiple of 28.